v m
Science Questions with Surprising Answers
Can one bit of light bounce off another bit of light?
 |
| Light-light scattering is possible through an indirect mechanism, but is extremely rare. Public Domain Image, source: Christopher S. Baird. |
Yes, one bit of light can bounce off another bit of light, but not directly, and the effect is very rare. Light is made out of small quantum objects called photons. When you turn on a lamp, the light bulb begins creating and emitting trillions upon trillions of photons. Photons are in a class of quantum particles known as bosons. Bosons are special because many bosons can occupy the exact same quantum state at the same time. Light being made of bosons is what makes a laser beam possible. A laser beam is a collection of many photons all in the same quantum state. In contrast, particles that are not bosons cannot occupy the same state at the same time. This is one of the effects that keeps the atoms in an object from collapsing to a single point. The principle that dictates that non-bosons cannot be in the same state is called the Pauli Exclusion Principle. Non-bosons are also called fermions. The fact that bosons such as light can occupy the same state means that they don't get in each other's way.
Also, light dominantly interacts with objects that have electric charge. Since light itself does not have electric charge, one photon cannot directly interact with another photon. Instead, they just pass right through each other without being affected. Because they are bosons and because they carry no electric charge, one photon cannot directly bounce off another photon. If you point one jet of water towards another jet of water, then at the point where they cross you will get a mess of water spraying all over due to the collisions. In contrast, if you shine one light beam such that it crosses another light beam, they will just pass through each other unaffected.
However, two photons heading towards each other can indeed collide indirectly. The process goes like this. A photon can spontaneously degenerate into a particle with mass and its antiparticle in a process known as pair production. In this process, the energy of the photon is completely transformed into the mass of the two particles. For example, a photon can turn into an electron and an anti-electron. If two photons head towards each other and they both turn into electron/anti-electron pairs at about the same time, then these particles can interact. The anti-electron from one photon will collide with an electron from the other photon, and turn back to light. The same thing happens to the other anti-electron and electron. The overall effect is that you get two photons going into the interaction and you get two photons coming out of the interaction, so it looks like the photons simply bounced off each other. In a sense, the one bit of light did indeed bounce off the other bit of light, but only indirectly by transforming into other particles.
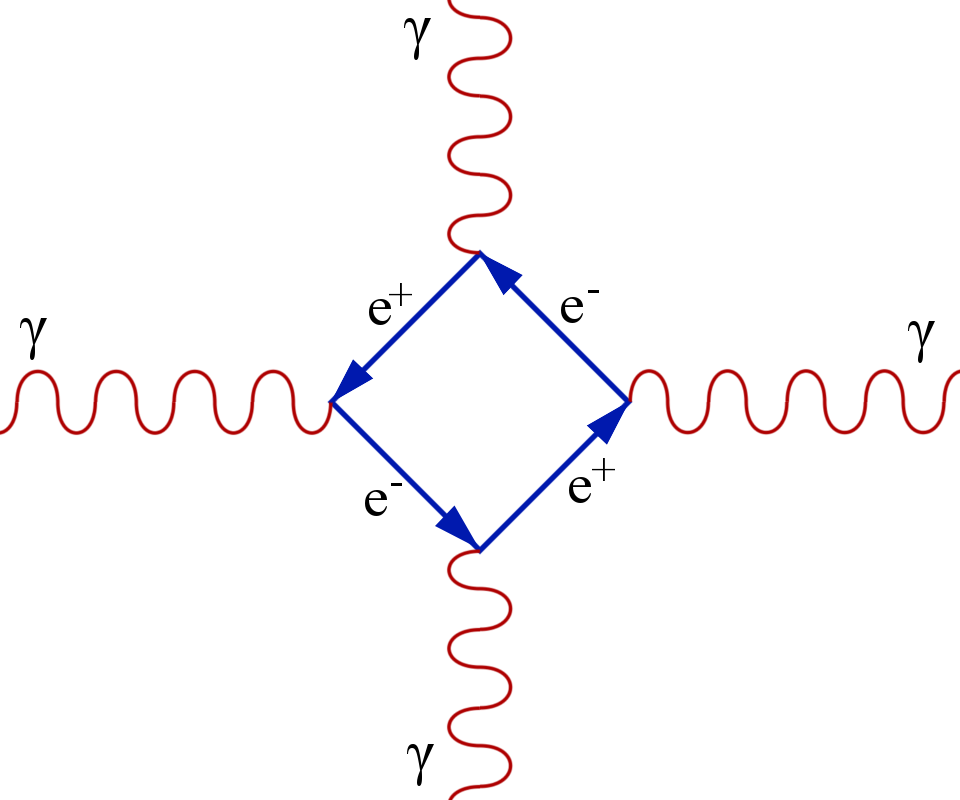
This interaction is shown in the diagram. The red squiggles represent photons, the e+ blue lines are anti-electrons (positrons), and the e- blue lines are electrons. A photon comes from the left of the diagram and decays into an electron and an anti-electron. At the same time, another photon comes from the right and turns into an electron and an anti-electron. Each anti-electron collides with an electron, they mutually annihilate and turn back into a new photon.
Photon-photon scattering is therefore possible through an indirect mechanism, but it is rare. There are two reasons that it is rare. First, light can only turn into other particles if it has enough energy to create the mass needed for the new particles, according to E = mc2. Because c is such a huge number, it takes a large amount of energy to make a little bit of mass. In order to turn into an electron and an anti-electron, the photon must have at least as much energy as the equivalent energy of their combined masses. Only gamma rays (one step higher than X-rays) have enough energy to do this. Secondly, the photons have to transform at just the right moment in order for the new particles from both photons to collide. For both of these reasons, light-light scattering is very rare. In fact, light-light scattering has never been conclusively observed. All the steps in light-light scattering have been observed (pair production and pair annihilation), so that we know that it is possible. The whole effect is just so rare that it has never been observed. However, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has both the ability to create high-energy light, and the ability to create a lot of it, making the rarity of light-light scattering more manageable. It is only a matter of time before the LHC observes light bouncing off light.







