Introduction to Arrays
For simplicity, we can think of an array a fleet of stairs where on each step is placed a value (let’s say one of your friends). Here, you can identify the location of any of your friends by simply knowing the count of the step they are on.
Remember: “Location of next index depends on the data type we use”.
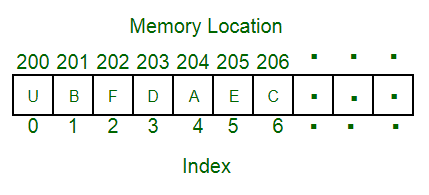
The above image can be looked as a top-level view of a staircase where you are at the base of staircase. Each element can be uniquely identified by their index in the array (in a similar way as you could identify your friends by the step on which they were on in the above example).
Types of indexing in array:
- 0 (zero-based indexing): The first element of the array is indexed by subscript of 0
- 1 (one-based indexing): The second element of the array is indexed by subscript of 1
- n (n-based indexing): The base index of an array can be freely chosen. Usually programming languages allowing n-based indexing also allow negative index values and other scalar data types like enumerations, or characters may be used as an array index.
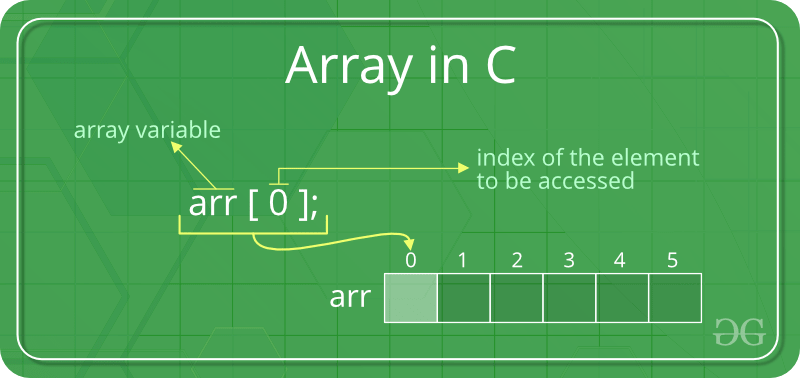
Advantages of using arrays:
- Arrays allow random access of elements. This makes accessing elements by position faster.
- Arrays have better cache locality that can make a pretty big difference in performance.
// A character array in C/C++/Java
char arr1[] = {'g', 'e', 'e', 'k', 's'};
// An Integer array in C/C++/Java
int arr2[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// Item at i'th index in array is typically accessed
// as "arr[i]". For example arr1[0] gives us 'g'
// and arr2[3] gives us 40.
Usually, an array of characters is called a ‘string’, whereas an array of ints or floats is called simply an array.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Your feedback is highly appreciated and will help us to improve our content.